A digital ledger is a type of ledger that is used to record financial transactions in a digital format. Unlike a traditional paper ledger, a digital ledger can be updated and accessed in real-time, making it a more efficient and secure way to track financial transactions.
Cryptocurrency transactions are often recorded on a digital ledger known as a blockchain. A blockchain is a de-centralized and public ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. Blockchains are secure by design and are an example of a Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Cryptocurrencies are popular because they offer a number of advantages over traditional fiat currencies. For one, cryptocurrencies are digital and global, making them more convenient and accessible than fiat currencies. They are also secure and transparent, thanks to the blockchain technology that powers them.
Digital ledgers are more popular than normal financial ledgers for a number of reasons. First, digital ledgers are more efficient and secure than traditional paper ledgers. Second, digital ledgers offer more transparency and accessibility than traditional financial ledgers. Finally, digital ledgers are more versatile and can be used for a variety of different applications.
What is Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)?
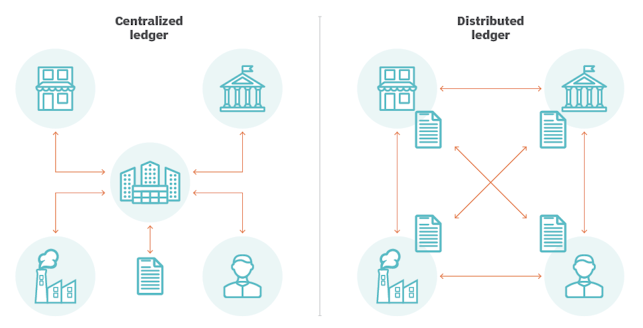
A computerised system for tracking asset transactions called distributed ledger technology (DLT) allows for the simultaneous recording of transactions and their associated information in numerous locations. Distributed ledgers don't have a central data store or management features, in contrast to conventional databases.
A distributed ledger generates a record of every item and establishes a consensus as to its authenticity since each node processes and validates every item. Both static data, like that in a registry, and dynamic data, such that in financial transactions, can be recorded on a distributed ledger.
Additionally, the technology generates an immutable database, meaning that information that has been stored cannot be removed and that any revisions are preserved permanently for posterity.
Distributed ledger technology examples:
There are several forms of distributed ledger technology in use today.
- The most well-known kind of DLT is blockchain, which groups transactions into blocks that are chained together and then broadcasts them to the network's nodes. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies are run by it.
- A different DLT called Tangle is targeted at IoT environments. The Tangle EE Working Group, which was established by the Eclipse Foundation and the IOTA Foundation, calls Tangle "a permission-less, fee-less, scalable distributed ledger, designed to support trustworthy data and value transmission between humans and machines."
The distributed ledger technologies Corda, Ethereum, and Hyperledger Fabric are also well-known.
Why Distributed Ledger Technology is Important?
Improved Record Keeping: By altering some of the principles of how businesses gather and share the data that goes into their ledgers, distributed ledger technology can significantly improve record-keeping.
Point of Control & Transparency: Consider Central Ledger, every place that provides data to the ledger has the potential to be a source of fraud or inaccuracies, making the process vulnerable to errors and manipulation. The accuracy of the data arriving from the other contributors cannot be effectively verified by any of the other participants who are providing data to the central ledger. With Distributed Ledger, real-time data sharing is made possible ensuring that the ledger is constantly up to date. In fact, each participating node can see these changes, it also promotes transparency.
Secure: It is inherently more secure since it does away with centralised ledgers' single point of failure and single target for hackers and manipulation.
Potential to Speed up transactions: Because there is no longer a need to go via a central authority or middleman, distributed ledger technology offers the potential to speed up transactions. DLT could also lower transaction costs in a similar manner.
However, there was one drawback the DLTs have been demonstrated to perform worse in some networking situations than centralised ledgers due to the high computational demands of running the highly decentralised verification process and disseminating copies of the ledger.
What are the few benefits of Distributed Ledger?
The use of distributed ledger technology in financial transactions has drawn a lot of early attention. That makes sense given that the bitcoin cryptocurrency became widely used while also demonstrating the viability of DLT. Early adopters of DLTs included banks and other financial institutions.
Digital ledger technology (DLT) supporters assert that businesses outside of finance can also use them. Governmental organisations are investigating how to document transactions like real estate title transfers using technology. DLT is being tested by healthcare organisations to enable a more effective method of updating patient records. For retaining supply chain data, many firms are testing DLT. And the legal industry is investigating how it can process and execute legal papers using DLT.
Additionally, according to experts, technology helps people gain better control over their personal information by enabling them to selectively disclose portions of their data as needed, restrict access to their records, and set temporal limits on how long information is accessible to third parties.
Digital ledgers, according to supporters, can also aid in keeping better track of intellectual property rights and ownership for goods like art, music, and movies, among other things.
Although DLT adoption is still in its early phases, the technology has already demonstrated in numerous instances its capacity to provide consumers with advantages, such as the following:
- High Visibility & Reliability
- Transparency Over Data Contributed to the Distributed Ledger
- Lower Operational Costs
- No Central Authority
- Faster Transaction Speeds
- Reduced Risks of Fraudulent Activity, Tampering and Manipulation
- High Level of Security
How the Blockchain and DLT relate and differ?
The terms distributed ledger technology and blockchain are often and even interchangeably used. They are not, however, the same.
Simply described, blockchain is a sort of distributed ledger technology, however not every distributed ledger technology employs blockchain technology.
This is unsurprising given how quickly interest in the technologies grew following the introduction of bitcoin and how interchangeable the technologies can be in actual application.
Using cryptography, both are used to establish decentralised ledgers. Both generate immutable records with time stamps. And both are thought to be practically unhackable.
Both can be public, allowing anybody to use them, as bitcoin is, or permissioned (private), limiting access to authorised users who agree to specified usage guidelines.
The main distinction is that blockchain uses blocks of data that are connected together to build the distributed ledger, as the name implies. However, DLT encompasses systems that establish a distributed ledger using various design concepts. The technology does not need to arrange its data in blocks to be deemed a DLT.
Conclusion:
It is unclear whether distributed ledger technologies, such as blockchain, will transform how governments, institutions, and industries operate.
Experts in this field advocate DLT as a critical technology that has the potential to not only improve existing processes but also to spark imaginative new applications.
Furthermore, they regard DLT as a component of the "internet of value," in which transactions take place in real time across worldwide networks. Indeed, digital ledger technology exists only because the internet, which enables it, is so widespread.
However, analysts anticipate that DLT adoption will follow the normal technology curve, with a few leaders out in front, followed by rapid followers, and finally by laggards. They also mention that enterprises encounter difficulties when it comes to deploying, growing, and operational-izing DLT.