Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is a form of digital record-keeping that uses a network of computers to store and share data. It is a type of distributed database that is maintained by multiple parties in a decentralised way. DLT is the foundation of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, but it can also be used to track and store other types of data, such as financial records, medical records, and legal documents.
What is a distributed ledger?
A distributed ledger is a type of digital database that is shared across a network of computers. It is designed to be secure and immutable, meaning that it cannot be changed or deleted. All participants in the network have access to the same data, which is updated and validated in real-time as new transactions occur.
What are the advantages of distributed ledgers?
The advantages of distributed ledgers include increased transparency, enhanced security, faster transaction times, and reduced costs. Additionally, distributed ledgers are resistant to tampering, making them more reliable than traditional databases.
How does distributed ledger technology work?
DLT works by using a network of computers to store and share data. Each computer in the network keeps a copy of the ledger, which is regularly updated and validated by all participants. This ensures that the data stored on the ledger is accurate and secure.
What are some applications of distributed ledger technology?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) has a wide range of potential applications, some examples include:
Supply Chain Management: DLT can be used to create a tamper-proof record of all the transactions that occur within a supply chain, making it possible to trace the origin of goods and ensure that they are not counterfeit.
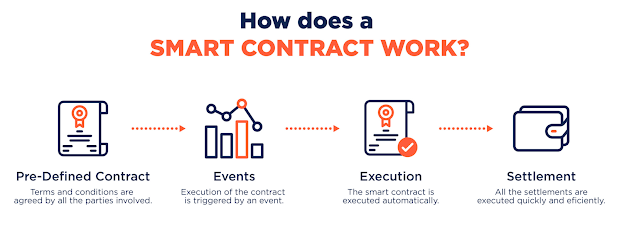
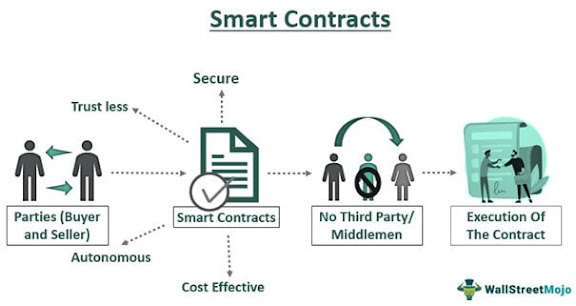
Smart Contracts: DLT can be used to create "smart contracts" which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code.
Identity Management: DLT can be used to create a decentralized system for storing and verifying identity information, enabling individuals to have more control over their personal data.
Digital Voting: DLT can be used to create a secure, transparent, and auditable voting system that allows for remote voting and prevents voter fraud.
Financial Services: DLT can be used to increase the efficiency and reduce the cost of financial transactions by creating a shared database of financial assets and enabling real-time settlement of trades.
Gaming and Digital collectibles: DLT can be used to create unique digital assets that can be owned and traded by players, creating new revenue streams for game developers.
Real estate: DLT can be used to create a tamper-proof record of property ownership, making it easier to buy, sell, and transfer property.
These are just a few examples, but the possibilities for DLT are vast and new use cases are constantly being developed.
What are some of the challenges associated with distributed ledger technology?
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) is a relatively new technology, and as such, it faces a number of challenges. Some of the main challenges include:
Regulation: DLT is a decentralised technology, and it is not yet clear how it should be regulated. Some governments have taken a cautious approach and have banned or restricted the use of certain types of DLT, while others have embraced it.
Security: DLT is a secure technology, but it is not immune to hacking and other forms of cyberattacks. As the technology develops, it will be important to continue to improve the security of DLT networks to protect users' data and assets.
Interoperability: DLT networks are not currently able to easily communicate with each other, making it difficult for users to move assets and data between different networks. This can be a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of DLT.
Adoption: DLT is a complex technology, and it can be difficult for non-technical users to understand and use. To achieve mainstream adoption, it will be necessary to develop user-friendly interfaces and applications that make DLT accessible to a wider audience.
Energy consumption: Some of the public blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum are consuming huge amount of energy which is a significant environmental concern.
Privacy and Confidentiality: While the transparency and immutability of DLT is one of its key advantages, it also raises concerns about privacy and confidentiality. This is a significant issue for industries that deal with sensitive data, such as healthcare and finance.
Overall, DLT is a promising technology with many potential benefits, but it will require ongoing research and development to address these challenges and fully realize its potential.
Conclusion:
By understanding how distributed ledger technology works and its potential applications, you can begin to explore the possibilities of this revolutionary technology. Whether you’re a developer, investor, or just an enthusiast, DLT has the potential to revolutionise the way we exchange data, assets, and value.