Blockchain technology has revolutionized the way we do business, manage our finances and interact with others. It has the potential to revolutionize virtually every industry and sector of the economy. If you’re looking to get ahead of the curve and understand the power of blockchain, then you’ve come to the right place. In this blog, I’ll explain what blockchain is, the key benefits of blockchain, how it works, the rise of the metaverse, different types of blockchain, smart contracts, cryptocurrency, the future of blockchain, adoption of blockchain technology, and courses to learn blockchain. So, let’s get started!
What is blockchain?
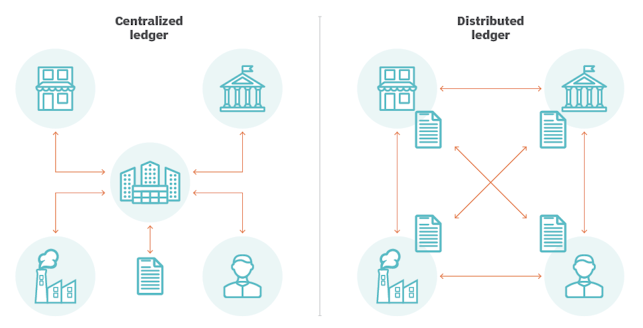
At its core, blockchain is a secure, distributed and immutable digital ledger technology (DLT). It is a decentralized system that records and stores data on a distributed ledger in a manner that is secure, transparent and tamper-proof. It is designed to be highly secure and efficient, making it ideal for transactions, data storage and tracking of assets.
Blockchain technology is based on cryptography, the science of writing and solving codes. Cryptography is used to secure and verify the transactions that take place on the blockchain. The data is stored in blocks, which are linked together in a chain. This chain of blocks makes up the blockchain. Every block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This makes it virtually impossible to alter the data without changing the entire chain.
The blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to disrupt the way we do business, manage our finances and interact with others. It is a decentralized system that allows users to securely exchange digital assets and conduct transactions without the need for a central authority.
Benefits of blockchain
Blockchain technology has many key benefits that make it attractive to businesses and individuals alike. Some of the key benefits include:
- Security: Blockchain technology is highly secure and tamper-proof, making it ideal for secure transactions.
- Transparency: All transactions on the blockchain are transparent and can be viewed by anyone with access to the network.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or reversed.
- Efficiency: Blockchain technology allows for faster and more efficient transactions, as well as a reduction in costs associated with processing transactions.
- Decentralization: The blockchain is decentralized, meaning there is no single point of failure or central point of control.
- Trust: The blockchain is highly trusted and secure, as it is based on cryptographic principles.
- Traceability: Transactions on the blockchain are traceable, meaning they can be tracked and audited.
How does blockchain work?
Blockchain technology works by using a network of computers to store and secure data. The data is stored in blocks, which are linked together in a chain. Every block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This makes it virtually impossible to alter the data without changing the entire chain.
The data is secured using cryptography, which is the science of writing and solving codes. Every transaction on the network is verified by the network of computers, making it virtually impossible to tamper with the data. The data is also encrypted, making it secure and private.
The blockchain is a decentralized system, meaning that it is not owned or controlled by any single entity. This makes it highly secure and resilient, as there is no single point of failure.
The rise of the metaverse
The rise of the metaverse is a term used to describe the virtual world created by blockchain technology. This virtual world is a decentralized platform where users can interact with one another and transact in digital assets without the need for a central authority.
The metaverse is a new type of digital economy, where users can create digital assets, exchange them and use them to purchase goods and services. This digital economy is powered by blockchain technology, which makes it highly secure and resilient.
The metaverse is the future of the digital economy and the possibilities are endless. From blockchain-based games to decentralized finance, the metaverse is revolutionizing the way we do business, manage our finances and interact with others.
Different types of blockchain
There are several different types of blockchain technology, each with its own benefits and uses. Some of the most popular types of blockchain include:
- Public blockchains: Public blockchains are open to anyone. They are highly secure and tamper-proof, as the data is stored on a distributed ledger.
- Private blockchains: Private blockchains are restricted to authorized users. They are used for internal transactions and data storage.
- Consortium blockchains: Consortium blockchains are a combination of public and private blockchains. They are used by organizations that need to securely store and share data with a select group of users.
- Hybrid blockchains: Hybrid blockchains are a combination of public and private blockchains. They are used to provide users with the benefits of both public and private blockchains.
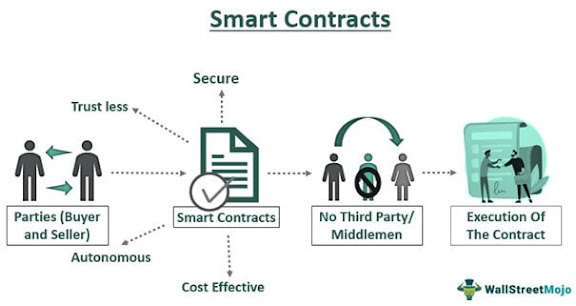
Smart contracts
Smart contracts are computer programs that execute automatically when certain conditions are met. They are used to facilitate, verify and enforce the performance of a contract. Smart contracts are self-executing, meaning they do not require a third party to enforce them.
Smart contracts are written in code, which makes them secure and tamper-proof. They are stored on the blockchain, which makes them immutable and resistant to tampering. Smart contracts are used for a variety of applications, including insurance, supply chain management and finance.
Cryptocurrency and blockchain
Cryptocurrency is a digital currency that is secured by cryptography. It is decentralized, meaning it is not owned or controlled by any single entity. Cryptocurrency is used to pay for goods and services, transfer money, and even to invest.
Cryptocurrency is powered by blockchain technology, which makes it secure and tamper-proof. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, meaning it is immutable and highly secure. Cryptocurrency is gaining popularity due to its low cost, fast transactions and secure nature.
The future of blockchain
The future of blockchain is bright. It has the potential to revolutionize virtually every industry and sector of the economy. From finance to healthcare to supply chain management, blockchain technology is being used to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase security.
The future of blockchain is also looking bright for businesses. Companies are already beginning to use blockchain technology to streamline operations, improve customer service, and reduce costs. As more and more companies begin to adopt blockchain technology, it is clear that the potential of this revolutionary technology is only just beginning to be realized.
Adoption of blockchain technology
The adoption of blockchain technology is growing at a rapid pace. Many businesses, organizations, and governments are beginning to see the potential of this revolutionary technology and are beginning to adopt it.
The potential of blockchain technology has led to the development of many new products and services. From blockchain-based games to decentralized finance, businesses are beginning to realize the potential of this technology and are using it to innovate and create new products and services.
Courses to learn blockchain
If you’re looking to learn more about blockchain technology, there are many courses available that can help you get started. These courses range from introductory courses to advanced courses and cover topics such as cryptography, blockchain fundamentals, smart contracts, and cryptocurrency.
These courses are designed to help you understand the fundamentals of blockchain technology and its applications. They will help you gain the knowledge and skills you need to start working with blockchain technology and develop your own projects.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize virtually every industry and sector of the economy. It is a secure, distributed and immutable digital ledger technology that is used to securely store and transfer data. It is highly secure and tamper-proof, making it ideal for secure transactions and data storage.
Blockchain technology has many key benefits, including security, transparency, immutability, efficiency, decentralization, trust, and traceability. It is being used in a variety of applications, from finance to healthcare to supply chain management.
The future of blockchain is bright, and the possibilities are endless. Companies are beginning to adopt blockchain technology and are using it to innovate and create new products and services. If you’re looking to learn more about blockchain technology, there are many courses available that can help you get started.
So, what are you waiting for? Unlock the power of blockchain and discover its revolutionary benefits! Start learning today and get ahead of the curve.