.webp)
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary technology that has been gaining a lot of attention recently. It is a distributed ledger technology that allows for secure, transparent, and immutable transactions between two or more parties. It is a decentralised system that does not rely on a central authority for verifying transactions. It is an open source platform, meaning anyone with the necessary coding skills can access the code and interact with it.
What is a Blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that can be used to record transactions between two or more parties. It is a form of a digital ledger that stores data in blocks that are chained together. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This data is stored across multiple computers or nodes, making it difficult to tamper with or corrupt. The nodes must come to a consensus to validate each transaction, ensuring its accuracy and validity.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain is a decentralised system, meaning that there is no central authority responsible for verifying transactions. Instead, the nodes in the network verify the transactions by coming to a consensus. This consensus is achieved through a process known as “mining.” Blockchain miners use specialised hardware to solve complex mathematical problems in order to validate the transactions. Once the miners have validated the transaction, it is added to the blockchain and can never be changed or reversed.
Let’s take an example of two users A and user B who are trying to make a transaction. The steps would be as follows:
Step-1: A initiates a transaction by creating a digital signature using their private key.
Step-2: The transaction is broadcast to the network and picked up by the miner.
Step-3: The miner verifies the transaction using A's public key and the digital signature.
Step-4: The miner then groups the transaction with other unconfirmed transactions into a block.
Step-4.1: The miner then competes with other miners to solve a complex mathematical problem called a "proof of work."
Step-4.2: The first miner to solve the problem gets to add the block to the blockchain, and in return, gets a reward in the form of newly minted bitcoins.
Step-5: Once the block is added to the blockchain, the transaction between A and B is considered confirmed.
Step-6: B can now check the blockchain to confirm that they have received the bitcoins from A.
Step-7: B can now spend the bitcoins in another transaction by following similar steps.
What are the benefits of Blockchain?
Blockchain technology offers several benefits that can improve efficiency, transparency, security, network distribution, traceability, and reduce costs. Some of the key benefits include:
Transparency: Blockchain provides a tamper-proof record of all transactions, making it easy to track and verify information.
Security: Blockchain's decentralised and distributed architecture makes it resistant to hacking and fraud.
Network distribution: Blockchain allows for decentralised networks, which can improve accessibility and reduce the risk of a single point of failure.
Traceability: Blockchain technology enables traceability of all transactions in the network, increasing accountability and enabling real-time tracking of goods and assets.
Reduced costs: Blockchain can reduce the need for intermediaries and streamline processes, resulting in cost savings.
Availability: Blockchain networks can be accessible globally, 24/7 with no downtime.
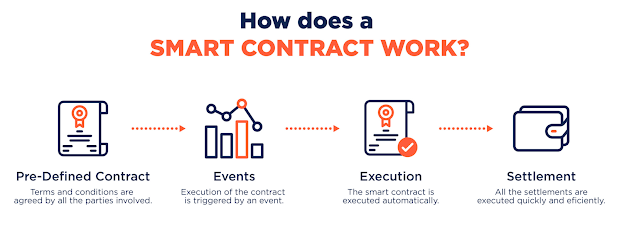
Automation: Blockchain smart contracts can automate many processes, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Decentralisation: Blockchain allows for the distribution of power and control, making the network more resilient and less vulnerable to manipulation.
Tokenisation: Blockchain technology allows for the creation of digital assets, such as tokens, which can be used as a means of exchange, representation of assets, or access to a network.
What are the realtime applications of Blockchain?
Blockchain technology has a wide range of potential applications as shown in the below picture:
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can be used to track products as they move through the supply chain, increasing transparency and efficiency. An example is IBM Food Trust, which uses blockchain technology to track the movement of food products from farm to store.
Voting Systems: Blockchain technology can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems, as votes can be recorded and tallied on the blockchain.
Digital Identity: Blockchain technology can be used to create secure digital identities, which can be used for a variety of purposes, such as logging into websites or accessing government services.
Real estate: Blockchain technology can be used to record and transfer property ownership, making the process more efficient and secure.
Banking: Blockchain technology can be used to increase the speed and security of financial transactions and settlement.
Healthcare: Blockchain can be used to securely store and share patient data and electronic medical records, allowing for better coordination of care and improved patient outcomes.
Gaming: Blockchain technology is being used to create new types of games, such as collectible card games that use non-fungible tokens (NFTs) to represent in-game items.
These are just a few examples of the many potential uses of blockchain technology.
Conclusion:
Blockchain technology is an innovative and disruptive technology that has the potential to revolutionise many industries. It is a secure, transparent, and immutable technology that can be used to facilitate secure and efficient transactions between two or more parties. As the technology continues to evolve, more use cases for blockchain will be discovered and the technology will become even more accessible and useful.
.webp)