Source: https://cdn.wallstreetmojo.com
The code and agreements contained within it live on distributed, decentralized blockchain networks. The terms of the contracts derive from blockchain users agreements to execute a program concurrently through a blockchain deployment system.
Once the contract is approved, it is deployed to the existing blockchain or another distributed ledger infrastructure. The prototype uses the Blockchain and smart contract technologies, and is designed to record the financial transactions within the terms of a building contract. There are different outcomes of this study resulting from developing the prototype of the contract management within financial activities using a cryptocurrency paradigm with the blockchain on various scenarios for the delivery of works at construction sites.
Smart contracts may also benefit from blockchain and other distributed ledger technologies for maintaining verifiable records of all activities related to executing complex processes, and which cannot be altered after the fact. The programs underlying smart contracts can be stored within the blockchain or other distributed ledger technologies, and integrated with a variety of payment mechanisms and digital exchanges, which may include Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. With blockchains, we can envision a world where contracts are embedded into digital code and stored on transparent, shared databases, where they are protected against removal, tampering, and modification by contracts themselves.
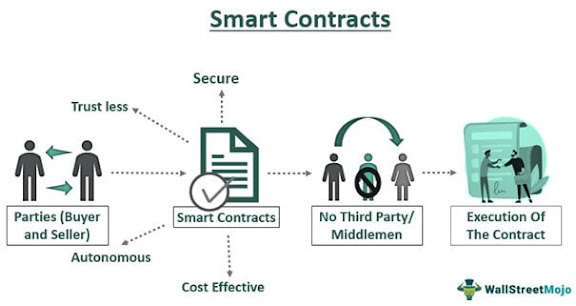
When embedded on blockchain, smart contracts allow for automatic enforcement of contractual terms in a deal, without an involving trusted third party. Just like a vending machine can automatically execute a contract for selling only physical goods contained in it, so too a smart contract built on blockchains can ensure the automatic execution of a contract that is related solely to transactions on blockchain-based assets (De Filippi & Mauro, 2017). Buterin (2013) proposed a decentralised platform for smart contracts on the basis of the blockchain in order to resolve any issues related to the execution context, and enable a global secure state.
In other jurisdictions worldwide, contracts are of varying legal status, and therefore, whether or not contracts written in code are legally binding depends on the countrys legal system. In other jurisdictions around the world, contracts have different status so whether a contract written in code is legally binding depends on the countrys legal system. Other legal challenges that could be mentioned are: (i) every country has their own laws and regulations, therefore, it is difficult to guarantee that it is compliant with all regulations, (ii) the terms of a law or conditions are not quantifiable, therefore, modeling those conditions into a smart contract is still difficult to make it relevant and quantifiable to the machines executing it, and (iii) governments are interested in the regulation and monitoring the usage of Blockchain technologies for a number of applications, which means the untrustworthy networks would fall back into a trust less third-party networks, which would therefore, therefore, losing some of their essence .
Other legal issues can be cited including:
(i) each country has its own laws and regulations, hence, it is complicated to ensure compliance will all regulations.
(ii) law clauses or conditions are not quantifiable, thus it is still complicated to model these conditions in smart contracts so that they are appropriate and quantifiable for a machine to execute them.
(iii) governments are interested in a regulated and controlled use of the blockchain technology in many applications, however, this means that the untrustworthy network will regress to a third-party trusted network, losing part of its essence [79 ].
Then, operationalisation is introduced to a cooperative web framework, showing steps for executing a smart contract, how actors interact with smart contracts, how operations are performed on a Blockchain network. The provision of smart contracts allows the greater blockchain value capture by setting up fixed transactions according to unique conditions (Angelis and Ribeiro da Silva 2019), a value feature for a network with multiple relationships and roles.
Cited Sources: